Difference between revisions of "Running OpenMower"
(Created page with "Now that you have your hardware assembled and the basic software installed on your mower, we can calibrate the magnetometer and start recordings maps and mowing the lawn. ==Prerequisites== In order to follow this guide, you will need the following: #A mower modified to run the OpenMower software #A working system image, where you can run the OpenMower software #An ssh connection to your mower #Optional, but very useful: A Linux PC where you can run RVIZ to visualize wh...") |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
#A working system image, where you can run the OpenMower software | #A working system image, where you can run the OpenMower software | ||
#An ssh connection to your mower | #An ssh connection to your mower | ||
#An Xbox GamePad | |||
#Optional, but very useful: A Linux PC where you can run RVIZ to visualize what your mower is doing | #Optional, but very useful: A Linux PC where you can run RVIZ to visualize what your mower is doing | ||
==Magnetometer Calibration== | ==Magnetometer Calibration== | ||
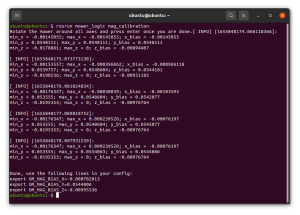
[[File:Mag Calibration.png|thumb|Example output of the mag_calibration node.]] | |||
The first step after finishing your assembly is to calibrate the magnetometer. This is important, because the magnets and metal parts embedded in the mower will interfere with the magnetic sensor. That's why it's important to '''do this after finishing the assembly!''' | The first step after finishing your assembly is to calibrate the magnetometer. This is important, because the magnets and metal parts embedded in the mower will interfere with the magnetic sensor. That's why it's important to '''do this after finishing the assembly!''' | ||
In order to start magnetometer calibration, start the OpenMower software on the mower using: | In order to start magnetometer calibration, start the OpenMower software on the mower using ssh: | ||
''roslaunch open_mower _comms.launch'' | |||
This will start the communication layer between ROS and the mower's hardware. | |||
Now start a second terminal and ssh into your mower. | |||
You can test, that the communication works by using the following command: | |||
''rostopic echo /mower/imu'' | |||
You should now see the raw IMU data printed to the terminal. If this is not the case, you have an error in your setup. | |||
Press CTRL+C to cancel the data display. | |||
Now you can start the calibration process by entering: | |||
''rosrun mower_logic mag_calibration'' | |||
Now rotate the mower '''slowly''' around all three axes. | |||
'''DON'T''' push the emergency stop button during the calibration. It has magnets embedded and will lead to '''wrong calibration.''' | |||
As soon as you're finished, press the enter button. The final values are printed to the terminal. | |||
Stop the first ROS process by pressing CTRL+C. | |||
You can copy and paste the values into your mower_config.sh. | |||
Now '''reload the mower_config.sh''' by entering: | |||
''source ~/mower_config.sh'' | |||
== Area Recording == | |||
Finally, you can record your mowing areas and the docking station position. | |||
I recommend that you start with a simple area with lots of space around first. This way if something goes wrong, your mower won't instantly crash. You will need to record at least one area and your docking station in order to start mowing. | |||
=== Overview === | |||
Basically, there are three things to record: The '''Navigation Area, Mowing Areas''' and the '''Docking Station position.''' | |||
* The '''mowing areas''' are the areas which will be mowed by the mower. Each mowing area consists of '''an outline''' and optionally '''areas to avoid'''. | |||
* The '''navigation area''' is the area which the robot may enter during navigation. This is needed to roam between mowing areas and also to find a way to the docking station, if it's not inside a mowing area. | |||
* The '''docking station''' is defined by a position and an orientation. Since the orientation of the mower is not 100% perfect due to magnetometer noise, we'll record two points which are then connected by a line. The direction of this line determines the docking orientation. More on that later | |||
=== Controls === | |||
During recording mode, you can move the mower and control the recording process using the Xbox game pad: | |||
* '''Hold A''' to move the mower using the '''left analog stick.''' Press '''RB for turbo mode.''' | |||
* '''Press B''' to start / stop recording of the current polygon. | |||
* '''Press Y''' to finish your current area and add it to the map. | |||
* '''Press X''' to record the first point of the docking position, '''Press X''' again to record the second position of the docking station and save it to the map. | |||
You start and stop the recording mode using buttons on the mower: | |||
* '''Press S1''' to start the recording mode | |||
* '''Press Home''' to stop the recording mode | |||
=== Recording the Mowing Areas === | |||
At first I like to record the mowing areas. Start with '''one area which is obstacle free.''' As soon as you are more confident in the mower's positioning, you can add more areas complex areas which may also be close to obstacles. | |||
In order to start recording an area, start the OpenMower software using: | |||
''roslaunch open_mower open_mower.launch'' | |||
Before starting the recording, make sure that you have a good GPS fix. You can do that by using the following command '''in a second terminal:''' | |||
''rostopic echo /ublox/navrelposned/accLength'' | |||
This will print the current GPS accuracy in '''0.1 mm''' steps. At full accuracy, you should get a value of 100. '''If it is larger, check your GPS config!''' | |||
Now, with the OpenMower software running and with a good GPS fix, you can start the area recording process. '''For this you will need a gamepad connected to your mower.''' Start the recording process by either pushing the S1 button on your mower or by executing the following command in a terminal to simulate the button press: | |||
~/open_mower_ros/utils/mower_buttons/press_s1.sh | |||
You should now be able to move your mower using the GamePad (see controls section above). | |||
Revision as of 22:24, 21 June 2022
Now that you have your hardware assembled and the basic software installed on your mower, we can calibrate the magnetometer and start recordings maps and mowing the lawn.
Prerequisites
In order to follow this guide, you will need the following:
- A mower modified to run the OpenMower software
- A working system image, where you can run the OpenMower software
- An ssh connection to your mower
- An Xbox GamePad
- Optional, but very useful: A Linux PC where you can run RVIZ to visualize what your mower is doing
Magnetometer Calibration
The first step after finishing your assembly is to calibrate the magnetometer. This is important, because the magnets and metal parts embedded in the mower will interfere with the magnetic sensor. That's why it's important to do this after finishing the assembly!
In order to start magnetometer calibration, start the OpenMower software on the mower using ssh:
roslaunch open_mower _comms.launch
This will start the communication layer between ROS and the mower's hardware.
Now start a second terminal and ssh into your mower.
You can test, that the communication works by using the following command:
rostopic echo /mower/imu
You should now see the raw IMU data printed to the terminal. If this is not the case, you have an error in your setup.
Press CTRL+C to cancel the data display.
Now you can start the calibration process by entering:
rosrun mower_logic mag_calibration
Now rotate the mower slowly around all three axes.
DON'T push the emergency stop button during the calibration. It has magnets embedded and will lead to wrong calibration.
As soon as you're finished, press the enter button. The final values are printed to the terminal.
Stop the first ROS process by pressing CTRL+C.
You can copy and paste the values into your mower_config.sh.
Now reload the mower_config.sh by entering:
source ~/mower_config.sh
Area Recording
Finally, you can record your mowing areas and the docking station position.
I recommend that you start with a simple area with lots of space around first. This way if something goes wrong, your mower won't instantly crash. You will need to record at least one area and your docking station in order to start mowing.
Overview
Basically, there are three things to record: The Navigation Area, Mowing Areas and the Docking Station position.
- The mowing areas are the areas which will be mowed by the mower. Each mowing area consists of an outline and optionally areas to avoid.
- The navigation area is the area which the robot may enter during navigation. This is needed to roam between mowing areas and also to find a way to the docking station, if it's not inside a mowing area.
- The docking station is defined by a position and an orientation. Since the orientation of the mower is not 100% perfect due to magnetometer noise, we'll record two points which are then connected by a line. The direction of this line determines the docking orientation. More on that later
Controls
During recording mode, you can move the mower and control the recording process using the Xbox game pad:
- Hold A to move the mower using the left analog stick. Press RB for turbo mode.
- Press B to start / stop recording of the current polygon.
- Press Y to finish your current area and add it to the map.
- Press X to record the first point of the docking position, Press X again to record the second position of the docking station and save it to the map.
You start and stop the recording mode using buttons on the mower:
- Press S1 to start the recording mode
- Press Home to stop the recording mode
Recording the Mowing Areas
At first I like to record the mowing areas. Start with one area which is obstacle free. As soon as you are more confident in the mower's positioning, you can add more areas complex areas which may also be close to obstacles.
In order to start recording an area, start the OpenMower software using:
roslaunch open_mower open_mower.launch
Before starting the recording, make sure that you have a good GPS fix. You can do that by using the following command in a second terminal:
rostopic echo /ublox/navrelposned/accLength
This will print the current GPS accuracy in 0.1 mm steps. At full accuracy, you should get a value of 100. If it is larger, check your GPS config!
Now, with the OpenMower software running and with a good GPS fix, you can start the area recording process. For this you will need a gamepad connected to your mower. Start the recording process by either pushing the S1 button on your mower or by executing the following command in a terminal to simulate the button press:
~/open_mower_ros/utils/mower_buttons/press_s1.sh
You should now be able to move your mower using the GamePad (see controls section above).